What is the difference between a homozygous and a heterozygous individual?
Humans have two sets of chromosomes. Homozygous and heterozygous are terms that are used to describe allele pairs. Individuals carrying two identical alleles (RR or rr) are known as homozygous. While individual organisms bearing different alleles (Rr) are known as heterozygous.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous Punnett?
When talking about Punnett squares, it is important to know what the terms heterozygous and homozygous mean. Heterozygous refers to a genotype with two different alleles (i.e. Bb, Rr, etc.) and homozygous refers to a genotype with two of the same alleles (i.e. BB, bb, etc.).
What is expressed in both homozygous and heterozygous individual?
A dominant allele can express itself in both the conditions, homozygous and heterozygous but recessive can be expressive only in homozygous condition.
What is the difference between heterozygous and heterozygous dominant?
If you’re heterozygous for a dominant disorder, you have a higher risk of developing it. On the other hand, if you’re heterozygous for a recessive mutation, you won’t get it. The normal allele takes over and you’re simply a carrier. This means your children may get it.
What are the two point of difference between homozygous and heterozygous?
Homozygous: You inherit the same version of the gene from each parent, so you have two matching genes. Heterozygous: You inherit a different version of a gene from each parent. They do not match.
What is the difference between a homozygous individual and a heterozygous individual quizlet?
Homozygotes have one chromosome while heterozygotes have two similar chromosomes. All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a heterozygote will differ. The homozygote will express the dominant trait and the heterozygote will express the recessive trait.
What is the difference between a heterozygous and a homogeneous gene?
Homozygous is when both of the alleles for a specific gene are the same (homo = same). Heterozygous is when the two alleles for a specific gene are different (hetero = different).
What is the difference between homologous and homozygous?
The difference between homologous and homozygous is that homologous refers to a degree of correspondence or similarity, whereas homozygous refers to an organism in which both copies of a given gene have the same allele. Answer: A homologous pair consists of two chromosomes that are very similar in size and shape.
Does heterozygous mean you have the disease?
Other heterozygous pairings would simply predispose a person to a health condition such as celiac disease and certain types of cancer. This doesn’t mean that a person will get the disease; it simply suggests that the individual is at higher risk. Other factors, such as lifestyle and environment, would also play a part.
What is meant by a heterozygous individual?
Listen to pronunciation. (HEH-teh-roh-ZY-gus JEE-noh-tipe) The presence of two different alleles at a particular gene locus. A heterozygous genotype may include one normal allele and one mutated allele or two different mutated alleles (compound heterozygote).
When two alleles are both expressed in the heterozygous individual?
Closely related to incomplete dominance is codominance, in which both alleles are simultaneously expressed in the heterozygote.
What is the difference between a homozygous and heterozygous individual?
An organism that has the same two copies of a gene is considered homozygous for that trait, while an organism that has different copies of a gene for a particular trait is considered heterozygous for that trait. In plant and animal breeding, such organisms can be called homozygotes and heterozygotes.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous Punnett squares?
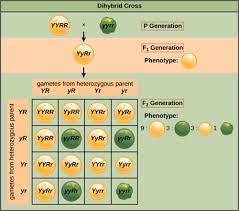
A Punnet square is a monohybrid cross and is going to be used to compare the traits of the example given earlier. For traits that have either two capital letters or two lowercase letters are known as a homozygous trait and for traits that have alternating letters are known as heterozygous traits.
Is homozygosity good or bad?
Increased risk of recessive genetic disorders: Homozygosity significantly heightens the risk of expressing recessive genetic disorders. In populations with increased levels of homozygosity, individuals are more likely to inherit two identical copies of a disease-causing allele from both parents.
What is an example of heterozygous?
What is an example of a heterozygous trait? A heterozygous genotype is a genotype that has multiple different alleles present in that gene. For example, a genotype that is “Tt” would be heterozygous, where the capital “T” could represent the trait of “tall” and the lowercase “t” could represent the trait of short.
What are the similarities between homozygous and heterozygous?
Expert-Verified Answer. If you are speaking of genetics, the only real similarity between the two is that they are terms used to describe alleles that are found on a particular gene. If you have homozygous alleles, then both of them are the same. If you have heterozygous alleles, then the two of them are different.
Who is known as the father of genetics?
As the father of modern genetics, Gregor Mendel is considered one of these giants owing to his discovery of the basic principles of inheritance.
What of the following correctly describes a difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals?
A particular genotype is described as homozygous if it features two identical alleles and as heterozygous if the two alleles differ.
How can you tell if an individual is homozygous or heterozygous for a certain trait?
To identify whether an organism exhibiting a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous for a specific allele, a scientist can perform a test cross. The organism in question is crossed with an organism that is homozygous for the recessive trait, and the offspring of the test cross are examined.
What does it mean if an individual is homozygous?
Homozygous, as related to genetics, refers to having inherited the same versions (alleles) of a genomic marker from each biological parent. Thus, an individual who is homozygous for a genomic marker has two identical versions of that marker.
What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous individuals?
In homogeneous, homo- means “same.” In heterogeneous, hetero- means “different” or “other.” In general use, the word homogeneous can describe something that is made up of parts or elements that are the same or very similar. It can also be used to describe two things as being the same or very similar in nature.
What is the difference between a homozygous and heterozygous gene quizlet?
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous? Homozygous is having two identical alleles for a particular gene. Heterozygous is having two different alleles for a particular gene.
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals mastering biology?
All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a heterozygote will differ. Since homozygotes carry two identical copies of a gene, all of the gametes will carry the same version. Heterozygotes have two different versions, so there will be two different types of gametes.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous individuals?
The terms Homozygous and Heterozygous are used to describe Allele pairs. A Homozygous individual carries a set of two identical (RR or rr) Alleles while a Heterozygous individual bears different Alleles (Rr).
What is the difference between heterozygous dominant and homozygous dominant?
An organism can be homozygous dominant, if it carries two copies of the same dominant allele, or homozygous recessive, if it carries two copies of the same recessive allele. Heterozygous means that an organism has two different alleles of a gene.
What is the difference between a heterozygous and a homogeneous gene?
Homozygous is when both of the alleles for a specific gene are the same (homo = same). Heterozygous is when the two alleles for a specific gene are different (hetero = different).
What is the difference between a homozygote and heterozygote?
To be homozygous for a trait is to have identical pairs of the genes (called alleles) that determine how it develops. To be heterozygous for a trait is to have different alleles for it. Being homozygous for a trait means that it will always turn out the same.
What is the difference between homozygous and homologous?
The difference between homologous and homozygous is that homologous refers to a degree of correspondence or similarity, whereas homozygous refers to an organism in which both copies of a given gene have the same allele. Answer: A homologous pair consists of two chromosomes that are very similar in size and shape.
What is a heterozygous individual?
Heterozygous, as related to genetics, refers to having inherited different versions (alleles) of a genomic marker from each biological parent. Thus, an individual who is heterozygous for a genomic marker has two different versions of that marker.
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals?
What is the difference between homozygotes and heterozygote?
Do all homozygotes carry the same version?
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous chromosomes?
So, let’s break it down. Imagine you have a pair of shoes. One shoe is blue, and the other is red. That’s kinda like heterozygous. You’ve got two different versions of the same gene.
Now, imagine you have two blue shoes. That’s homozygous. You have two identical versions of the same gene.
We use alleles to represent these different versions of a gene. An allele is a specific version of a gene. Let’s say the gene for eye color has two alleles: B for brown eyes and b for blue eyes.
Heterozygous: If someone has Bb, they have one allele for brown eyes and one allele for blue eyes.
Homozygous: If someone has BB, they have two alleles for brown eyes. And if someone has bb, they have two alleles for blue eyes.
So, homozygous individuals have two copies of the same allele, while heterozygous individuals have two different alleles.
Let’s bring this back to the shoes analogy. In the heterozygous example, you have one blue shoe and one red shoe. In the homozygous example, you have two blue shoes or two red shoes.
Think about it this way: You have two copies of every gene, one from your mom and one from your dad. These gene copies are called alleles. If you get the same allele from both parents, you’re homozygous for that trait. If you get different alleles from each parent, you’re heterozygous for that trait.
Now, you might be asking: How does this affect the trait being expressed?
Well, that’s where the concept of dominant and recessive alleles comes in.
A dominant allele is like the boss; it gets its way. If you have even one copy of a dominant allele, that’s the trait that gets expressed.
A recessive allele is like the shy one; it only gets its way if there’s no dominant allele around. If you have two copies of the recessive allele, that’s when the recessive trait is expressed.
Let’s go back to the eye color example. Brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. So, if someone has the Bb genotype, they will have brown eyes because the B allele is dominant. However, if someone has the bb genotype, they will have blue eyes because the b allele is recessive and there’s no dominant B allele to take over.
Homozygous dominant individuals express the dominant trait.
Homozygous recessive individuals express the recessive trait.
Heterozygous individuals express the dominant trait, even though they carry the recessive allele.
So, in short, homozygous means having two identical alleles for a trait, while heterozygous means having two different alleles for a trait. This affects how a trait is expressed because of the concept of dominant and recessive alleles.
FAQs about Heterozygous and Homozygous
What is a genotype?
A genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism. It’s the actual set of alleles an individual has for a specific trait. For example, the genotype for someone with brown eyes could be BB or Bb.
What is a phenotype?
A phenotype is the physical expression of a trait. It’s the observable characteristic, like brown eyes.
How are genotypes and phenotypes related?
The genotype determines the phenotype. The alleles you have (genotype) determine the physical trait you express (phenotype).
Can a heterozygous individual have a recessive phenotype?
No, a heterozygous individual cannot have a recessive phenotype. This is because they have at least one dominant allele, which will mask the recessive allele.
Can a homozygous individual have a dominant phenotype?
Yes, a homozygous individual can have a dominant phenotype. This is because they have two copies of the dominant allele.
Can a homozygous individual have a recessive phenotype?
Yes, a homozygous individual can have a recessive phenotype if they are homozygous recessive. This means they have two copies of the recessive allele, and no dominant allele to mask it.
What are some examples of traits that are influenced by dominant and recessive alleles?
There are many traits that are influenced by dominant and recessive alleles. Some examples include:
Eye color: Brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes.
Hair color: Dark hair is generally dominant over light hair.
Freckles: Freckles are dominant over no freckles.
Cleft chin: A cleft chin is dominant over a smooth chin.
Tongue rolling: The ability to roll your tongue is dominant over the inability to roll your tongue.
How does understanding homozygous and heterozygous help me in real life?
Understanding the difference between homozygous and heterozygous can be helpful for various reasons:
Understanding family history: If you know your family history, you can figure out your genotype for certain traits. For example, if you have blue eyes but your parents have brown eyes, you know you must be heterozygous for eye color.
Predicting offspring traits: If you know your genotype and your partner’s genotype, you can predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of your children.
Making informed decisions about your health: Certain genetic conditions are caused by recessive alleles. If you know your family history, you can talk to a doctor about your risk of developing these conditions.
Can you give me a real-life example of homozygous and heterozygous?
Sure! Let’s say you have a brown-haired mother and a brown-haired father, both heterozygous for hair color. The gene for hair color has two alleles: B for brown hair and b for blonde hair. Both parents have the Bb genotype.
When they have a child, there are four possible genotype combinations:
BB: Brown hair (homozygous dominant)
Bb: Brown hair (heterozygous)
bB: Brown hair (heterozygous)
bb: Blonde hair (homozygous recessive)
As you can see, there’s a 3 out of 4 chance that their child will have brown hair, and a 1 out of 4 chance that their child will have blonde hair.
And that’s the difference between homozygous and heterozygous individuals in a nutshell. It’s a pretty simple concept but it has huge implications for how traits are inherited and expressed.
Hopefully, this helped you understand the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals better. Now go forth and amaze your friends with your newfound knowledge!
MB: Ch 14 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? Heterozygotes carry two copies of a gene while homozygotes only carry one. Homozygotes have one chromosome while Quizlet
Bio ch 14 Flashcards | Quizlet
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a Quizlet
Chapter 14: Mendel & the Gene Idea Flashcards | Quizlet
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a Quizlet
Mastering Biology Chapter 14 Flashcards | Quizlet
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a Quizlet
Mastering Bio Ch 14 Flashcards | Quizlet
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? A. All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a Quizlet
genetics Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? a) Homozygotes have one Quizlet
Chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Who is considered the father of genetics?, What is the term, in genetics, for a specific characteristic?, What Quizlet
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous i
Homozygous individuals possess identical alleles at a specific gene locus, leading to uniform genetic makeup as homozygous dominant (AA) or recessive (aa). On the other Quizlet
Difference between Homozygous and Heterozygous
Start Quiz. Individuals carrying two identical alleles ( RR or rr) are known as homozygous. While individual organisms bearing different alleles (Rr) are known heterozygous. BYJU’S
Introduction to heredity review (article) | Khan Academy
A test cross can be used to determine whether an organism with a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous. Example test cross. Image credit: OpenStax , CC BY 4.0 Khan Academy
See more new information: curtislovellmusic.com
What Is The Difference Between Heterozygous And Homozygous Individuals?
Homozygous Vs Heterozygous Alleles | Punnet Square Tips
Homozygous Vs Heterozygous Genotype
Homozygous Vs Heterozygous
Gcse Biology – Dna Part 2 – Alleles / Dominant / Heterozygous / Phenotypes And More! #64
Genotype, Phenotype, Homozygous, Heterozygous, Homozygote, Heterozygote (Fl-Genetics/05)
Heterozygous Vs Hemizygous Genotype[ Alleles, Homozygous]
Differentiate Between The Following : Homozygous And Heterozygous Individual | Class 12 | Princi…
Link to this article: what is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals quizlet.
See more articles in the same category here: https://curtislovellmusic.com/category/what/