What is plastic deformation of polycrystalline material?
When polycrystalline materials are plastically deformed, not all grains are slipped simultaneously—the crystal grains are staged and slipped in batches through the application of external force. The main mechanism is the slip inside each grain, accompanied by the slip and rotation between the grains.
What defects always occur in a polycrystalline material?
In real polycrystalline materials, each grain has a specific crystal structure and orientation; very often crystal defects such as dislocations, stacking faults, twins, or vacancies exist which introduce distortions to the lattice structure.
Why are polycrystalline solids more advantageous than single crystals in the context of plastic deformation at ambient temperatures?
In polycrystalline materials, the presence of multiple grains and grain boundaries provides obstacles to dislocation motion during plastic deformation. As a result, the dislocations have to navigate through different crystal orientations and grain boundaries, leading to an increased resistance to deformation.
How is the grain structure of a polycrystalline metal altered when it is plastically deformed?
When a polycrystalline metal is plastically deformed the individual grains tend to rotate into a common orientation.
What is plastic deformation of a material?
Plastic deformation refers to the permanent distortion that occurs in a material when it is subjected to stresses that exceed its yield strength, causing it to elongate, compress, buckle, bend, or twist.
Are polycrystalline materials brittle?
When such fracture occurs, polycrystalline material shows a severe brittleness & poor ductility, irrespective of whether they are metallic, ceramics or intermetallics.
Does plastic deformation of a polycrystalline metal does not increase the density of the metal?
T/f; plastic deformation of a polycrystalline metal does not increase the density of the metal. True. Plastic deformation increases the dislocation density not the density.
Why polycrystalline materials are anisotropic?
The grain boundaries in polycrystalline materials have an important role in determining the overall properties of the material. Due to the differences in orientation of the grains, the properties of individual grains can be anisotropic (i.e., direction-dependent).
Why the properties of polycrystalline materials are most often isotropic?
For many polycrystalline materials the grain orientations are random before any working (deformation) of the material is done. Therefore, even if the individual grains are anisotropic, the property differences tend to average out and, overall, the material is isotropic.
What are the differences between single crystal vs polycrystalline systems?
This is explained in terms of the atomic scale periodicity: single crystals are periodic across their entire volume; polycrystals are periodic across individual grains; amorphous solids have little to no periodicity at all. The different atomic structures can have effects on the macroscopic properties.
Why monocrystalline is better than polycrystalline?
Monocrystalline solar panels tend to be more efficient in warm weather. Performance suffers somewhat as temperature goes up, but less so than with polycrystalline solar panels. Since they are monocrystalline and perform better in heat these panels are projected to have the longest life.
What causes plastic deformation in metals?
Plastic deformation of metals most commonly occurs as a result of the glide of dislocations, driven by shear stresses. (In some cases, deformation twinning may contribute, but this also requires shear stresses in a similar way, and also involves no volume change.)
What is the mechanism of plastic deformation of crystals?
In general the deformation of a single crystal in tension or compression consists of shear strain in which sheets of the crystal parallel to a crystal plane slip over one another, the direction of motion being some simple crystal-lographic axis.
What causes plastic deformation in polymers?
Under an applied stress these polymers plastically deform past their yield strength in a manner known as cold drawing. Cold drawing involves viscous flow where the chains slide past one another. Initially, the chains may be highly tangled but the applied stress forces them to elongate and align in a single direction.
What are the factors that affect plastic deformation?
Deformation often referred to strain, is the change in the size and shape of an object due to the change in temperature or an applied force. Depending on the size, material and the force applied, various forms of deformation may occur.
What is the mechanism of plastic deformation?
Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion that occurs when a material is subjected to tensile, compressive, bending, or torsion stresses that exceed its yield strength and cause it to elongate, compress, buckle, bend, or twist.
How to determine plastic deformation?
In the context of plastic deformation, the work done in stretching a material is calculated using the formula: Work done = stress / strain. B. The work done in stretching a material, in the context of plastic deformation, is calculated as: Work done = 2 x stress x strain.
What are the 2 most common ways in which plastic deformation occurs?
Plastic deformation occurs any time that the elastic limit of a material is exceeded. The most common places are impact/indentation events, and tensile/bending events. Any time the material does not return to its pre-stress state, there was plastic deformation.
What materials have high plastic deformation?
Plastic deformation is observed in most materials, particularly metals, soils, rocks, concrete, and foams. However, the physical mechanisms that cause plastic deformation can vary widely. At a crystalline scale, plasticity in metals is usually a consequence of dislocations.
What is the deformation plasticity theory?
6.2.2 Deformation Theory of Plasticity (6.20) may be simplified to yield a history-independent constitutive law for loading, or the deformation theory, that relates the current state of stress to the current state of strain. Such a loading is referred to as a proportional loading.
What is solidification of polycrystalline materials?
During the solidification of polycrystalline materials, small nuclei initially form at different positions of the liquid with random crystallographic orientations. These nuclei grow into larger crystals by absorption of atoms in surrounding liquid.
What is the difference between crystalline and polycrystalline materials?
In a single crystalline solid, the regular order extends over the entire crystal. In a polycrystalline solid, however, the regular order only exists over a small region of the crystal, ranging from a few hundred angstroms to a few centimeters.
What is the difference between ductile and brittle fracture in polycrystalline materials?
The stress needed to initiate a brittle crack is higher than the stress needed to grow the crack. It is this behaviour that distinguishes brittle fracture from ductile fracture, in which the stress to initiate a crack is lower than the stress to grow a crack.
What is plastic deformation of polycrystalline material?
When polycrystalline materials are plastically deformed, not all grains are slipped simultaneously—the crystal grains are staged and slipped in batches through the application of external force. The main mechanism is the slip inside each grain, accompanied by the slip and rotation between the grains.
Is plastic deformation brittle?
Brittle materials typically have low ductility and low toughness, whereas ductile materials, which undergo plastic deformation, have higher ductility and toughness.
Why does plastic deformation increase strength?
Work hardening, also referred to as strain hardening, occurs when a material is plastically deformed. It leads to an increase in dislocation density, resulting in improved yield strength and hardness. Work hardening is commonly employed in industrial processes to enhance the mechanical properties of materials.
Does plastic deformation of a polycrystalline metal does not increase the density of the metal?
T/f; plastic deformation of a polycrystalline metal does not increase the density of the metal. True. Plastic deformation increases the dislocation density not the density.
What is plastic deformation of nanomaterials?
With increasing plastic deformation the size of the cells decreases and the difference in the orientation increases. Through this process submicron- or nanocrystalline micro-structures develop. The controlling physical phenomena, materials- and processing parameters are one of the research topics at the ESI.
What is the plastic deformation of amorphous materials?
The plastic deformation of amorphous alloys is in fact composed of sections of elastic deformation. Each section of the elastic deformation is followed by local quick plastic shear deformation in the specimen to release stress.
What is plastic deformation of bearing?
Plastic deformations are found both on the raceways of the bearing rings and on the rolling elements (see illustration). Rolling over foreign bodies of all sizes causes plastic deformation. Material is displaced from the raceway by the penetration of the particles into the surface.
What happens when a polycrystalline material is plastically deformed?
What is the plastic deformation of a polycrystal?
Why is plastic deformation smaller than a single crystal?
Why is a uniform deformation in polycrystalline materials?
Let’s talk about plastic deformation in polycrystalline materials. This is a fascinating area of materials science, and understanding it is key to designing and using materials effectively.
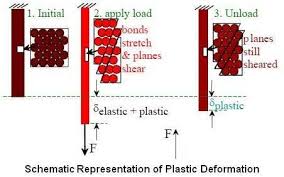
So, what are we talking about here? Imagine a solid material, like a piece of metal. When you apply force to it, it can deform, meaning it changes shape. This deformation can be elastic or plastic. Elastic deformation is temporary, and the material springs back to its original shape when the force is removed. Think of a rubber band. Plastic deformation, on the other hand, is permanent. The material doesn’t go back to its original shape. Think of bending a paperclip. Once it’s bent, it stays bent.
Now, let’s talk about polycrystalline materials. Most metals and ceramics are polycrystalline, meaning they’re made up of many tiny crystals, or grains, that are joined together. These grains have different orientations, and the way they interact with each other plays a big role in how the material deforms.
The Mechanisms of Plastic Deformation
When we talk about plastic deformation in polycrystalline materials, there are three main mechanisms we need to consider:
1. Slip: This is the most common mechanism. It involves the movement of dislocations through the crystal lattice. Dislocations are line defects in the crystal structure, and they act like a plane of atoms that has slipped out of place. When a force is applied, these dislocations move, causing the material to deform. Think of it like moving a rug across a floor. You can pull on the rug, but it’s easier to move it if you create a wrinkle or a fold (the dislocation) and then slide the wrinkle across the floor.
2. Twinning: This is a less common mechanism, but it can occur in some materials, particularly at low temperatures. It involves the formation of a mirror image of the crystal lattice across a specific plane. This essentially rearranges the atoms in the crystal, leading to deformation.
3. Grain boundary sliding: This mechanism is more important at high temperatures. It involves the sliding of one grain past another along their shared boundary. This movement is facilitated by the diffusion of atoms along the grain boundary.
Factors Affecting Plastic Deformation
The plastic deformation of a polycrystalline material is influenced by a bunch of factors, including:
Temperature: Higher temperatures generally make it easier for dislocations to move and for materials to deform plastically.
Strain rate: A higher strain rate, meaning the material is deformed more quickly, generally makes it harder for dislocations to move and for plastic deformation to occur.
Grain size: Smaller grains typically make the material stronger and more resistant to deformation. This is because there are more grain boundaries, which act as barriers to dislocation movement.
Crystal structure: Some crystal structures are more prone to plastic deformation than others. For example, materials with a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure, like aluminum and copper, are generally more ductile than those with a body-centered cubic (BCC) structure, like iron.
Alloying: Adding other elements to a metal can change its plastic deformation behavior. For example, adding carbon to iron makes it stronger and less ductile.
Importance of Plastic Deformation
Understanding plastic deformation in polycrystalline materials is crucial in many applications:
Material design: Engineers use this knowledge to design materials with specific properties. For example, they can design materials that are strong and ductile by controlling the grain size and adding alloying elements.
Manufacturing: Many manufacturing processes rely on plastic deformation, such as rolling, forging, and extrusion. Understanding how materials deform allows engineers to optimize these processes and create products with the desired shape and properties.
Predicting material behavior: By understanding how plastic deformation works, engineers can predict how materials will behave under different conditions, such as high temperature or stress. This is vital for designing safe and reliable structures and components.
FAQs about Plastic Deformation of Polycrystalline Materials
Q: What is the difference between plastic and elastic deformation?
A:Elastic deformation is temporary, and the material returns to its original shape when the force is removed. Plastic deformation is permanent, and the material remains deformed even after the force is removed.
Q: How does grain size affect plastic deformation?
A: Smaller grains generally make a material stronger and more resistant to plastic deformation. This is because there are more grain boundaries, which act as barriers to dislocation movement.
Q: What is the role of dislocations in plastic deformation?
A:Dislocations are line defects in the crystal structure, and their movement is the primary mechanism for plastic deformation in many materials. They act like a plane of atoms that has slipped out of place, and their movement allows the material to deform without breaking.
Q: What is the difference between slip and twinning?
A:Slip involves the movement of dislocations through the crystal lattice. Twinning involves the formation of a mirror image of the crystal lattice across a specific plane, rearranging the atoms and leading to deformation.
Q: How does temperature affect plastic deformation?
A: Higher temperatures generally make it easier for dislocations to move, which can lead to increased plastic deformation. This is because the thermal energy allows the atoms to vibrate more, making it easier for dislocations to overcome barriers and move through the crystal lattice.
Q: What is the difference between ductile and brittle materials?
A:Ductile materials can undergo significant plastic deformation before they fracture. Brittle materials fracture with little or no plastic deformation. This difference is often related to the mechanisms of plastic deformation and the presence of defects in the material.
Q: What are some examples of materials that exhibit plastic deformation?
A: Metals, such as aluminum, copper, and steel, are known for their ability to undergo significant plastic deformation.
This overview provides a good foundation for understanding the plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials. It’s a complex field, and there’s always more to learn, but I hope this introduction has given you a good starting point.
See more here: What Defects Always Occur In A Polycrystalline Material? | Plastic Deformation Of Polycrystalline Materials
Stages of plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials
The stages of deformation of the polycrystalline metallic materials were generalised for the first time in the well-known monographs. The chapter describes the eight-stage pattern of plastic flow of the metallic polycrystals that has been experimentally determined. Taylor & Francis eBooks, Reference Works and Collections
Deformation of Single Crystals, Polycrystalline Materials, and Thin …
Thus, the plastic deformation of the polycrystal is smaller than that of the single crystal. When polycrystalline materials are plastically deformed, not all grains National Center for Biotechnology Information
Plastic Deformation and Strain Localizations | SpringerLink
Plastic deformation of a polycrystalline material is restricted to individual grains with different orientations separated by grain boundaries, which all together Springer
Dislocation motion in plastic deformation of nano polycrystalline
The plastic deformation of nano polycrystalline composites includes four stages: the annihilation of adjacent dislocations on grain boundaries, the absorption of Springer
Microstructural deformation process of shock
Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials under shock wave loading is a critical characteristic in material science and engineering. Nature
Deformation of Single Crystals, Polycrystalline Materials, and Thin …
slip are the basic plastic deformation mechanisms of polycrystalline materials. Although defects can hinder lattice dislocations and increase material strength, they also reduce mdpi-res.com
Plasticity without dislocations in a polycrystalline
We demonstrate by MD simulations that this material can undergo large plastic deformation without the aid of dislocations. Nature
The plastic deformation of polycrystalline aggregates
For a number of metallic polycrystalline aggregates, it is shown experimentally that [sgrave] f, the flow stress at constant strain, is related to the grain Taylor & Francis Online
(PDF) Deformation of Single Crystals, Polycrystalline
slip are the basic plastic deformation mechanisms of polycrystalline materials. Although defects can hinder lattice dislocations and increase material strength, they also reduce the… ResearchGate
See more new information: curtislovellmusic.com
Mse 201 S21 Lecture 23 – Module 3 – Deformation In Polycrystalline Materials
Lecture 12 Part 1 – Defects In Crystalline Materials – 7 (Plastic Deformation)
Deformation In Single Crystal And Polycrystalline Materials – Deformation – Material Technology
Plastic Deformation Of Polycrystalline Metals Part I#Gate Metallurgy
Understanding Plastic Deformation Mechanisms | Skill-Lync
Dislocation Mechanism In Single Crystals And Polycrystals / Polycrystalline Materials
Lecture 1_Crystal Structure Slip And Twinning Deformation
55. Grain Boundaries In Polycrystalline Materials
Link to this article: plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials.
See more articles in the same category here: https://curtislovellmusic.com/category/what/